 The bore of the cannula is 24G. The 24G is sufficiently wide to easily deliver the anesthetic solution.
The bore of the cannula is 24G. The 24G is sufficiently wide to easily deliver the anesthetic solution.- The tip is blunt and slightly flattened. The tip is blunt so that it will not penetrate the eye ball. The flat tip facilitates the smooth entry of the cannulaa into the sub-Tenon’s space.
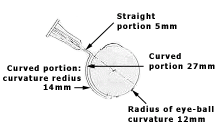
- The straight portion is 5 mm long. The straight portion is 5 mm long so that it will be stiff and long enough to visualize this portion when the curved portion of the cannula is completely in the sub-Tenon’s space.
- The radius of curvature of the curved portion is 14 mm. As the average radius of the eye ball is 12 mm, it helps the cannular to almost hug the eye ball and remains precisely in the sub-Tenon’s space.
- The curved portion is 27 mm long. When it enters at a point 5 mm from the limbus, in an average eye, the tip will be 5 mm away from the optic eye.
- The junction between the straight and the curved portion indicates the exact point at which the penetration of the cannula should be stopped.
- When the straight portion of the cannula(and the syringe) is radial to the eye ball and is 5 mm away from the limbus, it indicates that the curved portion of the cannula is in the right tissue plane (sub-Tenon’ space about 5 mm away from the optic nerve.
